Sports Nutrition
The Basics of Sports Nutrition
Diet plays a vital role in providing adequate energy for physical activity and daily functions. The type, amount, composition and timing of food intake can dramatically affect performance and recovery from exercise, specifically the food that is eaten before and after training and competition. Since higher volume training or high intensity exercise (CrossFit) stresses the body, proper nutrition and fluids are needed for recovery.
Proper nutrition can:
- Help you train longer at higher intensity
- Improve recovery and reduce fatigue
- Improve strength and body composition
- Improve or help maintain immune function
- Reduce the change for stomach discomfort during workouts
- Improve overall performance
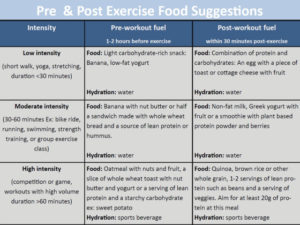
Here are some suggestions for pre and post workout meals based on duration and level of intensity of exercise.
Remember, a good workout does not give you permission to eat whatever you want. Make an effort not to “reward” your workout with high-calorie or unhealthy foods. Replenish with healthy protein, carbohydrates and fluids. The work you put into your workouts is reflected through good nutrition.
References:
- Dunford, M. (2010). Fundamentals of sport and exercise nutrition. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics.
- Williams, M. (2010). Nutrition for health, fitness & sport (9th ed.). Boston, Mass.: McGraw-Hill.
- How to Fuel Your Workout. (n.d.). Retrieved January 21, 2015, from http://www.eatright.org/Public/content. aspx?id=6442471759
- Position of The American Dietetic Association and The Canadian Dietetic Association: Nutrition for physical fitness and athletic performance for adults. (2009). Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 691-696.